The holding time of aluminum extruded profiles is mainly determined by the solid solution rate of the strengthened phase. The solid solution rate of the strengthened phase is related to the quenching heat temperature, the nature of the alloy, the state, the section size of the aluminum profile, the heating conditions, the medium and the number of furnace loading factors.
When the general quenching heat temperature is inclined to the upper limit, the holding time of aluminum is correspondingly shorter; After high temperature extrusion, deformation degree is larger, the holding time is shorter. For the pre-annealed aluminum profile, because the strengthening phase is slowly precipitated and coarser, the dissolution rate of the strengthening phase is slower, so the holding time is correspondingly longer.
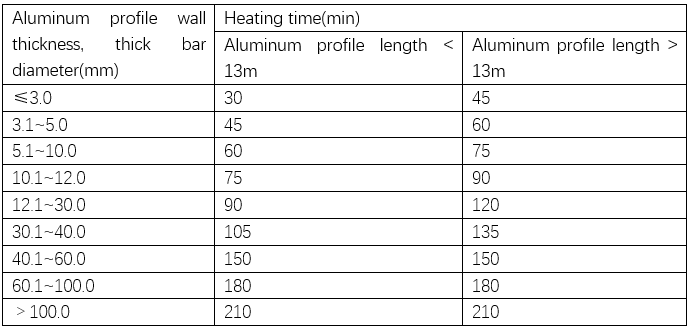
The holding time of aluminum profiles heated in hot air is very different from that in salt baths, and the heating time in salt baths is much shorter. Most industrial aluminum profiles or bars use vertical air quenching furnaces, and the holding time is calculated when the metal surface temperature or furnace temperature reaches the lower limit of the quenching temperature. Table 1 lists the heating and holding times of aluminum profiles and bars of different sizes in a vertical air quenching furnace.
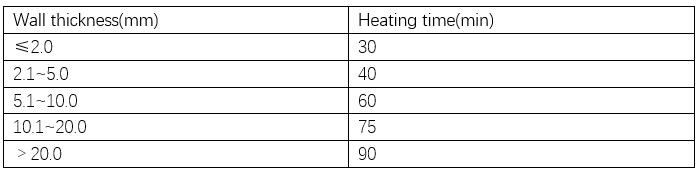
Table 2 shows the heating and holding time of pipes with different wall thicknesses in the vertical air quenching furnace. The holding time of quenching heat must ensure that the strengthening phase is fully dissolved in order to obtain the maximum strengthening effect, but the heating time should not be too long, in some cases, it will reduce the performance of the profile.
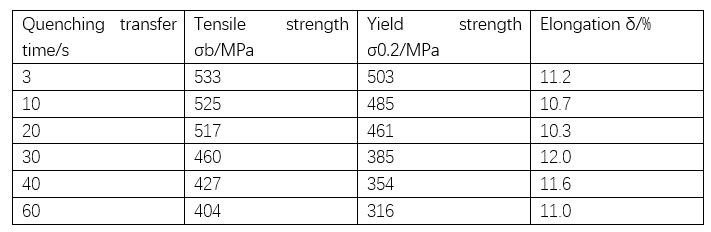
Many industrial heat-treated aluminum profiles such as 2A12, 7A04 and other high-strength profiles cannot be quenched in air like architectural aluminum profiles such as 6063 alloy, that is, a small cooling rate can prevent the precipitation of strengthening phases. They are taken out of the quenching heat furnace, transferred to the quenching water tank, and cooled in the air for just a few seconds, there will be precipitation of strengthening phases, which will affect the strengthening effect. Table 3 lists the effects of different transfer times of 7A04 alloy on the mechanical properties after quenching.
(Table 3 – 7A04 alloy quenching transfer time effect on the mechanical properties of aluminum profiles)
Therefore, the quenching transfer time is one of the process parameters that must be specified in the quenching process of aluminum profiles, that is, the transfer of aluminum profiles from the quenching furnace to the quenching medium must be completed within the specified maximum transfer time, which is called the maximum allowable transfer time or quench delay time. This time is related to the composition of the alloy, the shape of the profile, and the degree of automation of the equipment operation. If conditions permit, the shorter the quenching transfer time, the better. The general process regulations: the transfer time of small profiles should not exceed 20s, large or batch quenched aluminum profiles should not exceed 40s; for superhard profiles such as 7A04, the transfer time should not exceed 15s.
Edited by May Jiang from MAT Aluminum
Post time: Oct-21-2023